| admgmt.msc | AD 管理 |
| azman.msc | 授權管理員 |
| certmgr.msc | 憑證管理員 |
| certtmpl.msc | 憑證範本 |
| ciadv.msc | 索引服務程序 |
| comexp.msc | 元件服務 |
| compmgmt.msc | 電腦管理 |
| devmgmt.msc | 裝置管理員 |
| dfrg.msc | 磁碟重組工具 |
| dfsgui.msc | 分散式檔案系統 |
| dhcpmgmt.msc | DHCP 管理 |
| diskmgmt.msc | 磁牒管理 |
| dnsmgmt.msc | DNS 管理 |
| domain.msc | AD 網域及信任 |
| dsa.msc | AD 使用者及電腦 |
| dssite.msc | AD 站台及服務 |
| eventvwr.msc | 事件檢視器 |
| fsmgmt.msc | 共用資料夾管理 |
| gpedit.msc | 群組原則 |
| iis.msc | IIS 管理 |
| ipaddrmgmt.msc | IP 位址管理 |
| lusrmgr.msc | 本機使用者和群組 |
| mscorcfg.msc | .NET 設定 |
| ntmsmgr.msc | 卸除式存放裝置 |
| ntmsoprq.msc | 卸除式存放裝置管理員請求 |
| perfmon.msc | 效能檢視器 |
| pkmgmt.msc | 公開金鑰管理 |
| rsadmin.msc | 遠端存放 |
| rsop.msc | 原則結果組 |
| schmmgmt.msc | Schema 管理 |
| secpol.msc | 本機安全性設定 |
| services.msc | 服務 |
| tapimgmt.msc | 電話語音 |
| tsmmc.msc | 遠端桌面 |
| uddi.msc | UDDI服務主控站 |
| winsmgmt.msc | WINS 管理 |
| wmimgmt.msc | WMI 管理 |
11/30/2011
讓人看來專業的 Windows *.msc 指令
11/27/2011
設定 Red hat Enterprise Linux bonding 介面.
設定Red hat Enterprise Linux bonding 介面流程如下:
- 確認主機上至少有兩張網卡.
- 編輯或新增4個檔案:
- 編輯 /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
- 編輯 /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth1
- 新增 /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-bond0
- 新增 /etc/mdoprobe.d/bonding.conf
- 重新啟動網路服務.
- 確認 bond0 介面,是否啟用.
- 查看目前 bond0,使用之實體網路埠.
- 手動切換 bond0,使用之實體網路埠.
我們接著看每個步驟較詳細的設定/檢查方法.
- 確認主機至少有兩張網卡.
[root@XXOOXp ~]# dmesg | egrep 'eth.:'
e1000: eth0: e1000_probe: Intel(R) PRO/1000 Network Connection
e1000: eth1: e1000_probe: Intel(R) PRO/1000 Network Connection
- 編輯或新增4個檔案:
- 編輯 /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 的內容.
[root@XXOOXp network-scripts]# cat ifcfg-eth0
DEVICE=eth0
BOOTPROTO=static
MASTER=bond0
SLAVE=yes
ONBOOT=yes
- 編輯 /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth1 的內容.
[root@XXOOXp network-scripts]# cat ifcfg-eth1
DEVICE=eth1
MASTER=bond0
SLAVE=yes
ONBOOT=yes
- 新增 /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-bond0
[root@XXOOXp network-scripts]# cat ifcfg-bond0
DEVICE=bond0
IPADDR=192.168.75.55
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
ONBOOT=yes
BOOTPROTO=static
BONDING_OPTS="mode=1 miimon=50"
- 新增 /etc/mdoprobe.d/bonding.conf
[root@XXOOXp modprobe.d]# cat bonding.conf
alias bond0 bonding
- 編輯 /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 的內容.
- 重新啟動網路服務:
[root@XXOOXp ~]# service network restart
- 確認 bond0 介面,是否啟用.
[root@XXOOXp ~]# ip addr show bond0
5: bond0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,MASTER,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue
link/ether 00:0c:29:0f:d7:c6 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.75.55/24 brd 192.168.75.255 scope global bond0
inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:fe0f:d7c6/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
- 查看目前 bond0,使用之實體網路埠.
[root@XXOOXp ~]# cat /proc/net/bonding/bond0
Ethernet Channel Bonding Driver: v3.4.0 (October 7, 2008)Bonding Mode: fault-tolerance (active-backup)
Primary Slave: None
Currently Active Slave: eth0
MII Status: up
MII Polling Interval (ms): 50
Up Delay (ms): 0
Down Delay (ms): 0Slave Interface: eth0
MII Status: up
Link Failure Count: 0
Permanent HW addr: 00:0c:29:0f:d7:c6Slave Interface: eth1
MII Status: up
Link Failure Count: 0
Permanent HW addr: 00:0c:29:0f:d7:d0
[root@XXOOXp ~]# - 手動切換 bond0,使用之實體網路埠.
[root@XXOOXp ~]# ifenslave --change-active bond0 eth1
[root@XXOOXp ~]# cat /proc/net/bonding/bond0 | egrep 'Currently'
Currently Active Slave: eth1
參考資料:
Network Card Bonding On CentOS (bonding 不同 mode 的說明)
8.2.2. Channel Bonding Interfaces
[root@XXOOXp ~]# modinfo bonding
[root@XXOOXp ~]# man modprobe.conf
11/09/2011
sed and perl 的網站
備查用..
以後要認真看~~
sed 快速參考
http://sed.sourceforge.net/sed1line.txt (英文)
http://sed.sourceforge.net/sed1line_zh-CN.html (中文)
perl 參考
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/linux/library/l-p102/index.html
10/13/2011
如何檢查 RHEL 5.X and AIX 的網卡連接狀態?
How to check RHEL 5.x (or above) and IBM AIX NIC link status?
這個是滿實用的一個功能...
有時人不在機器旁邊又不確定線到底有沒有接,
又或是線到底有沒有感應到...就會派上用場了!
關於 RHEL 5.x (或以上),可透過下面的指令..
[xxooxp ~]# ethtool eth0 | egrep 'Link'
Link detected: yes
或是
[xxooxp ~]# mii-tool –v eth0
而在IBM AIX上,可透過下面的指令
root@aix61 / # netstat -v | egrep '(ETHERNET|Link)'
ETHERNET STATISTICS (ent3) :
Logical Port Link State: Up
Physical Port Link State: Down
ETHERNET STATISTICS (ent2) :
Logical Port Link State: Up
Physical Port Link State: Down
ETHERNET STATISTICS (ent0) :
Link Status : Up
ETHERNET STATISTICS (ent1) :
Link Status : UNKNOWN
9/25/2011
讓 shell 幫你轉換 2, 8, 16 進位至10進位
測試過 bash 及 ksh 均有此功能。
# 2進位轉10進位
$ echo "Convert 2 to 10: $((2#11111111))"
Convert 2 to 10: 255
# 8進位轉10進位
$ echo "Convert 8 to 10: $((8#377))"
Convert 8 to 10: 255
# 16進位轉10進位
$ echo "Convert 16 to 10: $((16#ff))"
Convert 16 to 10: 255
參考資料
linux Shell script - 16進位轉10進位, 8進位轉10進位,2進位轉10進位
AIX版的Linux watch指令...(監控指令的輸出狀態)
標題有些繞舌...不過不影響我們的主題需求...
Linux上有個好用的指令叫做watch,
能夠持續的監控指令的輸出狀態,讓系統管理員能夠隨時嘗握狀況。
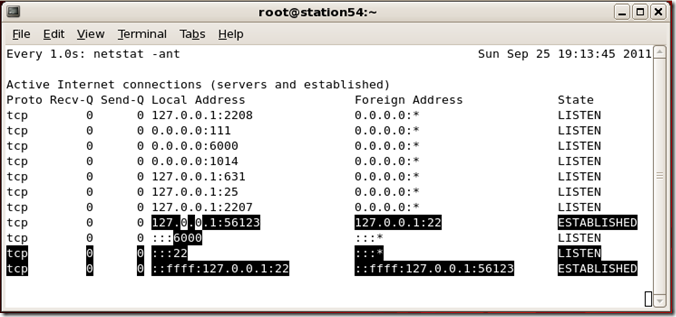
比方說我們想要監控 netstat -ant 的輸出狀況,隨時觀查連線狀態的變化。
則可以使用
# watch -d -n 1 ‘netstat –ant'
-n 表示每一秒更新一次輸出。
-d 表示將有變更的部份以高亮標示(Highlight)
輸出如下圖
很方便對吧!!
可惜...在IBM AIX上沒有這個好東西...( AIX上的watch指令是別的奇怪用途..)
不過別擔心! 因為這種問題在網路上早就一堆解答了...
這篇只是把他們整理一下,方便日後查找而已 ;-)
AIX 上的 watch 指令替代方案
其實也不難! 就是寫個迴圈來一直進行~
root@aix # cat watch.sh
#!/bin/ksh
#
# $1 = 監控的間隔時間,以秒為單位.
# $2 = 請將所有要輸入的指令以雙引號(")或單引號(')包起來.
#
# Exit the watch.sh use Ctrl + C
#
while true
do
clear
echo "Interval $1 sec, Command: $2"
eval $2
sleep $1
done
root@aix # #以下比方說要執行監控ls -l /home/user | grep .profile,每秒更新一次.
root@aix #
root@aix # ./watch.sh 1 "ls -l /home/user | egrep '.profile'"
參考資料如下:
Monitoring logs and command output
9/12/2011
製作 AIX rootvg 的 mirror
以下適用於 AIX 4.3.3, AIX 5.1, AIX 5.2 及 AIX 5.3。
- 確認有空的硬碟可以做 mirror (假設是 hdisk1)
- cfgmgr
- lsdev -Cc disk
- 加入 hdisk1 至 rootvg 使用 "extendvg rootvg hdisk1"
- 輸入 "mirrorvg rootvg" 來執行 mirror
- 把VG Quorum關閉chvg -Qn rootvg
- 修改開機清單如下 (其實 AIX 也會提示你做)
- 先看現在的開機順序 bootlist –o –m normal
- 修改順序 bootlist –m normal hdisk0 hdisk1
- 執行 bosboot 對 hdisk0, hdisk1 建立開機檔案
- bosboot -a
- 重新開機。 (聽說5300-07後不必重新開機)
參考資料:
tar 指令備份小技巧
tar 可以透過 pipe line 做一些特別的備份方式。
像是使用
[root@/tmp]# tar -cvf - /etc | tar -xvf -
這邊以|(pipe line)為分隔說明兩部份,
前半部的參數是
| c | 建立被 tar 的資料。 |
| v | verbose 的意思,就是會顯示 tar 了什麼。 |
| f | 這個參數後要接 tar 完後的檔名,比方說 tar –cvf backup.tar 要tar的來源 |
| - | 這符號是表示標準輸入或標準輸出,要看使用的位置,這邊的例子是標準輸出。 |
因此前半部就是叫 tar 指令將 /etc 內的所有資料,tar 到 – (標準輸出)內。
後半部的參數是
| x | 解開被 tar 的資料。 |
| v | verbose 的意思,就是會顯示 tar 了什麼。 |
| f | 這個參數後要接 tar 完後的檔名,比方說 tar –xvf backup.tar 解tar的目地 |
| - | 這符號是表示標準輸入或標準輸出,要看使用的位置,這邊的例子是標準輸入。 |
所以後半部就是讓 tar 指令將 – (標準輸入,將前半部的標準輸入拿來用),
內的資料解 tar 到目前所在的目錄(因為我們沒在最後”解tar的目的”中輸入參數)。
或者是
# (cd source-Folder ;tar -cf - .)|(cd target-Folder ; tar -xBpf –)
7/27/2011
Storage 雜記
近期的SSD硬碟,在Storage system遇到效能上瓶頸時,常常可能會被提出來改善 Storage 效能上瓶頸,
但我們在認為 Storage 遇到瓶頸的時候,
可能需要了解一下一些名詞
Read Hit / Write Hit
Read Miss / Read Miss
一般來說,我們的主機若有連接至Storage system,則其資料的讀 / 寫有些部份是會依靠 Storage System 的 Cache 來完成。
當主機的資料寫到 Storage 的 Cache 後,主機就會覺的 OK,這個資料寫入了。
(接下來Storage會自已把資料從Cache寫入後端的磁碟。)
而當主機要讀 / 寫的資料直接就在 Storage System Cache中時,則就是稱為 Read Hit, Write Hit。
若主機要讀 / 寫的資料不在 Storage System Cache 中時,則稱為 Read miss, Write miss。
假設我們的 Storage System Cache 非常大,則資料永遠在 Read hit, Write hit 的狀態..
Storage System 的效能會非常好...
這也就是說若Storage System Cache非常大,則資料是不會需要到後端的硬碟做讀 / 寫,因為在 Cache 的地方就完成了。
但現實來說,Storage System Cache 通常不會非常大,因此到達某一程度的時候,主機的讀 / 寫資料就會常常發生 read miss, write miss ,而 SSD 硬碟的存在,正好可以解決這個問題。
就資料的讀寫性能來說。Storage System Cache > SSD > FC > SAS > SATA
因此,若我們在考慮加裝 SSD 硬碟前,可能需要考慮 Storage System Cache 是否足夠...
因為若是我們的資料90%都是在 Storage System Cache 中讀寫完成,
則其實 SSD 發揮的作用只是剩下的 10%而已…
7/11/2011
Accessing the IBM ASMI using a Web browser
摘錄自 System Hardware information Center
POWER7 Accessing the ASMI using a web browser
POWER6 Accessing the ASMI using a web browser
POWER6及POWER7的共同注意事項:
If you plan to connect your server to your network, this PC or notebook temporarily connects directly to the server for setup purposes only. After setup, you can use any PC or notebook on your network that is running Netscape 9.0.0.4, Microsoft Internet Explorer 7.0, Opera 9.24, or Mozilla Firefox 2.0.0.11 as your ASMI console.
Note: Complete the following steps to disable the TLS 1.0 option in Microsoft Internet Explorer to access the ASMI using Microsoft Internet Explorer 7.0 running on Windows® XP:
- From the Tools menu in Microsoft Internet Explorer, select Internet Options.
- From the Internet Options window, click the Advanced tab.
- Clear the Use TLS 1.0 check box (in the Security category) and click OK.
POWER6及POWER7適用的ASMI Default IP
以下為POWER5專用
POWER5 Accessing the ASMI using a web browser
7/10/2011
vi 及 sed 置換字串的小技巧
工作中常常會需要將設定檔或script內的很多字替換掉,
當然這本身是一個很簡單的事情。
比方檔案內容如下:
[xxooxp@blogsopt ~]# cat xyz.txt
/uuu/abc
/uuu/abc
/uuu/abc
/uuu/abc
而我們想將 uuu 置換為 xyz 可透過簡單的幾個方法達成。
使用 vi 置換,
[xxooxp@blogsopt ~]# vi xyz.txt
/uuu/abc
/uuu/abc
/uuu/abc
/uuu/abc
~
~
:1,$s:/uuu/:/xyz/:g
使用 sed 置換
[xxooxp@blogsopt ~]# sed –i ‘s:/uuu/:/xyz/:g’ xyz.txt
7/08/2011
檢查 Windows 記憶體大小 (DIMM size)及實體CPU數量(CPU socket counts)
這個方法應可適用於Windows 2003以上之版本。
先啟動命令提示字元,接著輸入以下指令。
C:\>wmic
wmic:root\cli>/NAMESPACE:CIMV2
wmic:root\cli>CPU LIST BRIEF
Caption DeviceID Manufacturer MaxClockSpeed Name SocketDesignation
Intel64 Family 6 Model 23 Stepping 10 CPU0 GenuineIntel 2534 Intel(R) Core(TM)2 Duo CPU P8700 @ 2.53GHz None
wmic:root\cli>MEMORYCHIP LIST BRIEF
Capacity DeviceLocator MemoryType Name Tag TotalWidth
4294967296 DIMM 1 0 Physical Memory Physical Memory 0 64
4294967296 DIMM 2 0 Physical Memory Physical Memory 1 64
wmic:root\cli>
5/06/2011
使用 IBM Dynamic System Analysis (DSA) 蒐集 ESXi 主機硬體 Log
IBM 官方的 Log 蒐集工具,IBM Dynamic System Analysis (DSA) 可使用在 Linux, Windows, VMware ESX等平台。
而要蒐集 VMware ESXi 也是可以的,只要透過以下參數 (下列使用 Windows 版 DSA 示範):
以下是在命令提示字元:
C:\>ibm_utl_dsa_dsyt85t-3.40_portable_windows_x86-64.exe –h
注意下面這個參數的說明
--vmware-esxi <userid:password@IP [:port]>
Retrieve system information from the remote target system loaded
with VMWare Embedded Hypervisor.
C:\>ibm_utl_dsa_dsyt85t-3.40_portable_windows_x86-64.exe --vmware-esxi root:password@192.168.1.1
上例假設 ESXi 主機的帳號為 root 密碼為 password , @後為 ESXi 主機 IP。DSA 會使用 TCP 5989 與 ESXi 主機溝通。並將 Log 蒐集至本機的 C:\IBM_Support 目錄。
5/02/2011
1/07/2011
RHEL Login shells v.s. non-login shells
Login Shells
- Login Shells 使用的 Startup scripts 如下順序: (紅色只有 Login shells 才有)
- /etc/profile (global configuration)
- /etc/profile.d/*.sh
- $HOME/.bash_profile (user configuration)
- $HOME/.bashrc
- /etc/bashrc
- 有哪些是 Login Shells ?,任何在登入時建立的 shells,舉例有
- Virtual Console (Ctrl + Alt F1 ~ F6)
- X Login
- Remote Login (SSH, Telnet …etc.)
- su -
- 用 su - 切換時使用者也是 login shells。
Non-Login Shells
- Non-Login Shells 使用的 Startup scripts 如下順序:
- $HOME/.bashrc
- /etc/bashrc
- /etc/profile.d/*.sh
- 有哪些是 Non-Login Shells ?,沒有登入的 shells (打帳號 / 密碼),舉例有
- su
- graphical terminals.
- any other bash instances.
- executed scripts.
應用方式
依 Login shells 與 Non-Login shells 使用不同 Startup script 的特色,來做一些環境變數(Environment variables)的調整。
1/05/2011
更改 RHEL Virtual Console 解析度
Change Virtual Console Resolution
參考下表:
| Color | 640 x 480 | 800 x 600 | 1024 x 768 | 1280 x 1024 | 1600 x 1200 |
| 256 | 769 | 771 | 773 | 775 | 796 |
| 32 k | 784 | 787 | 790 | 793 | 797 |
| 64 k | 785 | 788 | 791 | 794 | 798 |
| 16 M | 786 | 789 | 792 | 795 |
編輯 /boot/grup/menu.lst 檔,找到類似下一行的東西,
kernel /vmlinuz-2.6.18-164.el5 ro root=LABEL=/ rhgb quiet vga=788
加入粗體字的部份,即設定解析度為800 x 600。
建議可以先在 GRUB 開機的時候,先用編輯的測試 OK 後在寫到 menu.lst 檔。
參考資料:
[SOLVED] how to set video mode at boot
Console Resolution: VGA Values
Kernel source:
/usr/share/doc/kernel-doc-*/Documentation/fb/vesafb.txt
/usr/share/doc/kernel-doc-*/Documentation/svga.txt